Hotlinking is the act of using another site’s bandwidth by displaying their website asset – like an image, video, or audio file – on a different site via a direct web link.
In this situation, the original website owner is responsible for covering and paying for these server resources each time a web browser requests and loads the asset.
You might have heard of hotlinking if you’re a web user or a site owner. It is often considered bad practice by webmasters because it puts websites at a significant disadvantage.
For example, website B’s owner found a funny meme on Website A and decided to use it on their website. But instead of saving the image on their computer and reuploading it, the owner of Website B links the image directly from Website A to instantly show it on their site.
Even though people can see the meme on Website B’s site, the origin server is still storing it. In other words, server resources from Website A are used every time a user views the hotlinked image. If Website B receives high traffic, a significant amount of A’s server resources will be used.
This article will explain why you should avoid hotlinking and how to stop doing it. For web administrators, we provide four methods to protect your website from hotlinks: using cPanel, an FTP client, a content delivery network (CDN), and WordPress plugins.
Hotlinking: Why you should avoid it
There’s no denying that hotlinking has the most negative effects on website owners. Hotlinking might seem like an easy way to acquire website assets, but in reality, it can also cause them harm.
Here are the five main reasons why you should avoid hotlinking at all costs:
- Unauthorized reuse of assets is unethical. Unauthorized reuse of content assets is theft. You must obtain permission and rights to use the content unless it is under the creative commons license.
- You would be stealing resources from another website owner and increasing their hosting costs. A hotlinked image consumes a considerable amount of bandwidth on the origin server every time it is viewed. Therefore, the perpetrator is not only stealing content, but also stealing website resources from the original owner.
- Hotlinking can have legal repercussions. Legal and monetary consequences can follow hotlinking copyrighted content. If the original owner sends the perpetrator a copyright infringement notice and the perpetrator does not respond, the original owner can file a lawsuit.
- There is no control over the hotlinked file. Hotlinked images are connected to the original website. In the event that the original owner decides to modify or delete the content at any time, the changes will also appear on the perpetrator’s website.
- The act of hotlinking is unprofessional. As a result of hotlinking’s bad reputation, adopting this practice can negatively affect your reputation. You may be perceived as lacking originality and not respecting other users’ rights.
Hotlinking: How to stop it
Now that you know why you should stop hotlinking, you may be wondering what you can do instead if you would like to use images from other websites.
The most important thing is to make sure you have the right to use the image. You can sometimes obtain images by asking the owner for permission. There are some that are under strict legal license, such as copyrighted photos.
As soon as you receive permission or have handled the legal process, you should upload the file to your own server or use a third-party provider. For images, use an image hosting service like Imgur. In this way, you won’t be stealing bandwidth from the original website owner.
For whatever reason, you may not be able to acquire the image you want. Here are some alternatives:
- Find a similar replacement. You might still be able to convey the same message with a different image. Try acquiring a similar photo if you can’t get a specific one from another source, such as a stock image service like Unsplash, Shutterstock, or Pexels.
- Link the page, not the image. If you can’t replace the image with a similar alternative, you may want to include a link to the original web page. You might not be able to show the image exactly as you wanted, but your visitors will still be able to see it by clicking on the link you provided.
Hotlinking: How to prevent it
In order to prevent content and bandwidth theft, it is very important to implement hotlink protection.
It is important to remember that hotlink protection will not harm your website’s search engine ranking. Your search engine optimization (SEO) efforts will remain unaffected as long as you don’t prevent search engines from indexing your images.
Here are few ways to prevent your assets from being hotlinked.
Method 1: Accessing cPanel Settings
Hotlink protection can be enabled directly through cPanel. The process should be similar for other control panels. Follow these steps:
- Log in to your hosting account and head to the cPanel dashboard.
- Under Security, select Hotlink Protection.
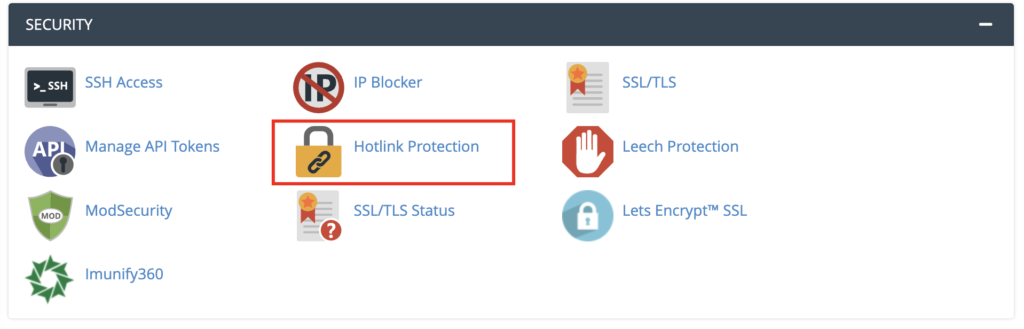
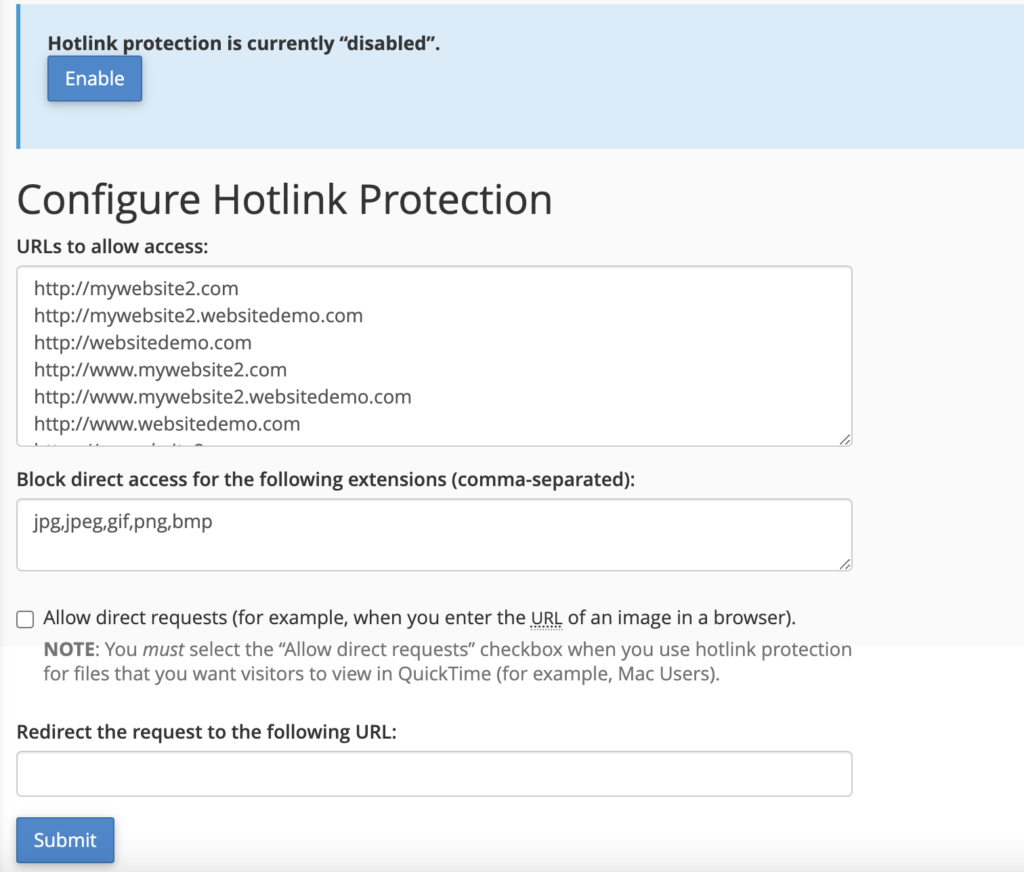
- Under Block direct access to these extensions, choose which file extensions you would like to protect. Once applied, visitors won’t be able to view the direct links attached to the file extensions you’ve selected.
- In the Redirect blocked requests to this url field, you have the option to enter the URL of an error page you want to show visitors who attempt to hotlink your website.
Method 2: Using an FTP Client
Another option is to edit your website’s .htaccess file by accessing it through an FTP client like FileZilla or the file manager on your hosting account’s control panel.
Keep in mind that this method involves editing your website’s code, so be careful – a small error can render your site unusable.
- Once you’ve connected to your website’s FTP or opened up the file manager, navigate to the public_html folder.
- Within the public_html folder, find the .htaccess file and download it.
- On your computer, make a copy of the original .htaccess file in case something goes wrong.
- Open the .htaccess file using your preferred text editor.
- Copy and paste the following code into the file:
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^$
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^http(s)?://(www\.)?google.com [NC]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^http(s)?://(www\.)?bing.com [NC]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^http(s)?://(www\.)?yahoo.com [NC]
RewriteCond %{HTTP_REFERER} !^http(s)?://(www\.)?yourdomain.com [NC]
RewriteRule \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$ – [NC,F,L]- Change yourdomain.com to your site’s actual domain.
- Save the edited .htaccess file and upload it back to the public_html folder.
Method 3: Using a CDN
Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) for your website has many benefits. A CDN can increase content delivery speed, providing better performance for your visitors. It can also offer asset management features for website administrators, hotlink protection being one of them.
The process of activating hotlink protection will vary depending on the CDN provider you use. The following tutorial will go over how to set up hotlink protection on two popular CDN providers – Cloudflare and KeyCDN.
Here’s how to activate hotlink protection on Cloudflare:
- Log in to your Cloudflare account and navigate to the dashboard.
- Select the Scrape Shield app, which is located on the right of the apps bar.
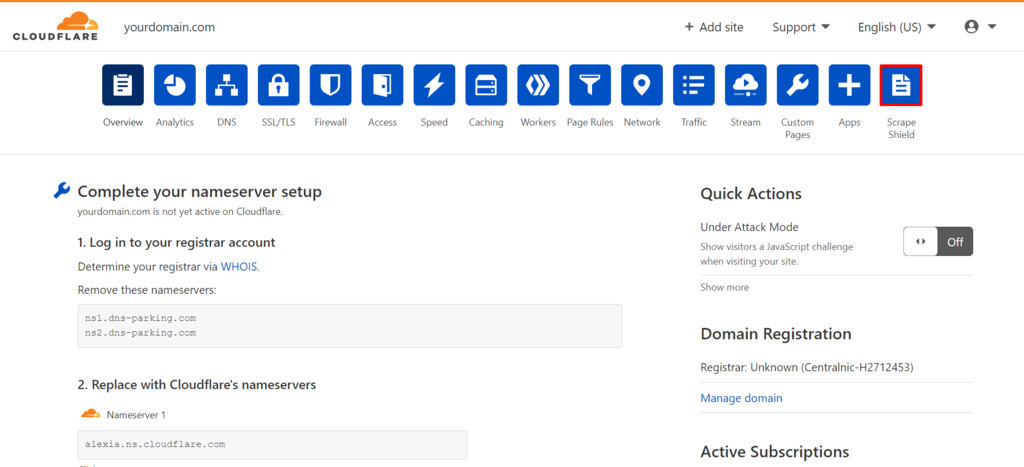
3. Switch Hotlink Protection on.
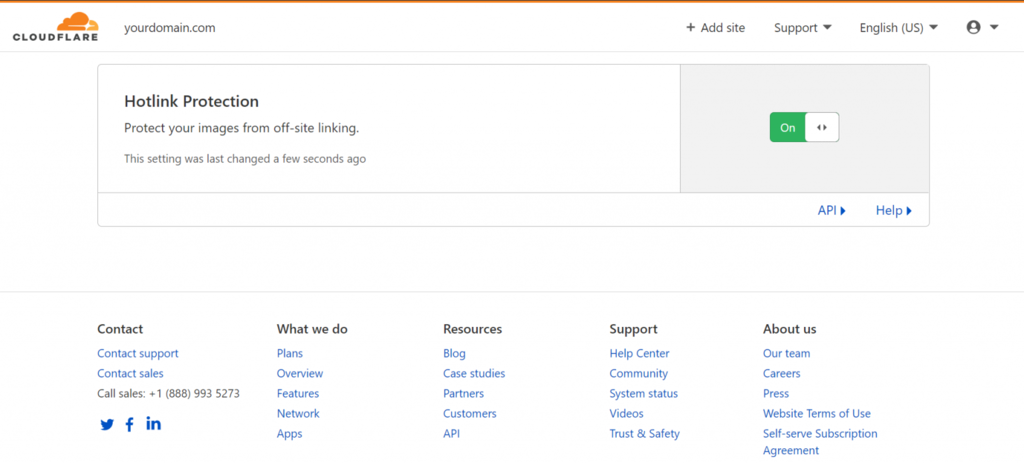
The Scrape Shield app by Cloudflare specifically prevents image hotlinking and supports .gif, .ico, .jpg, .jpeg, and .png file types.
Here’s how to activate hotlink protection on KeyCDN:
- Log in to your KeyCDN account and go to the dashboard.
- Select Zone Referrers from the sidebar.
- Click Add Zone Referrer.
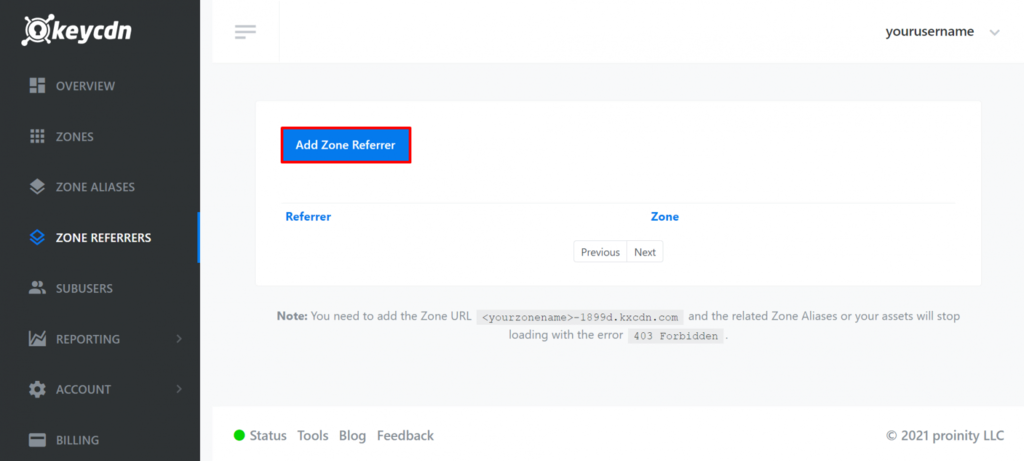
- Enter the URL of the zone referrer. Zone referrers are the URLs that are allowed to view direct links of your website assets. URLs that aren’t included in the zone referrers will be blocked.
- Select the Zone from the drop-down menu.
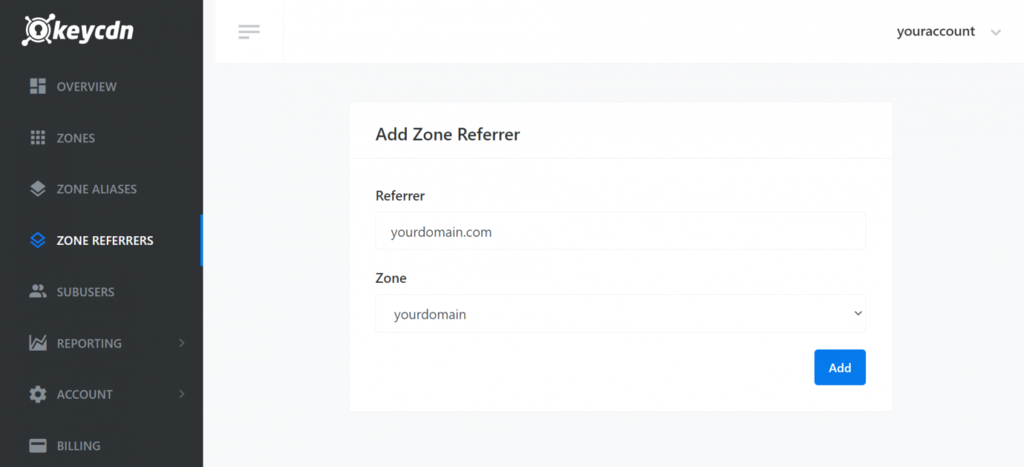
- Click Add to save your settings.
- Feel free to add multiple zone referrers.
Method 4: Using a WordPress Plugin
If you use WordPress as your website’s content management system (CMS), there are several WordPress plugins available that can prevent hotlinking. We’ll go over three of them.
The first one is the All In One WP Security and Firewall plugin, which can automatically edit your website’s .htaccess file to prevent hotlinks. Follow these steps to set it up:
- From the WordPress dashboard, install the plugin and activate it.
- Navigate to the WP Security menu -> Firewall -> Prevent Hotlinks.
- Select Check this if you want to prevent hotlinking to images on your site.
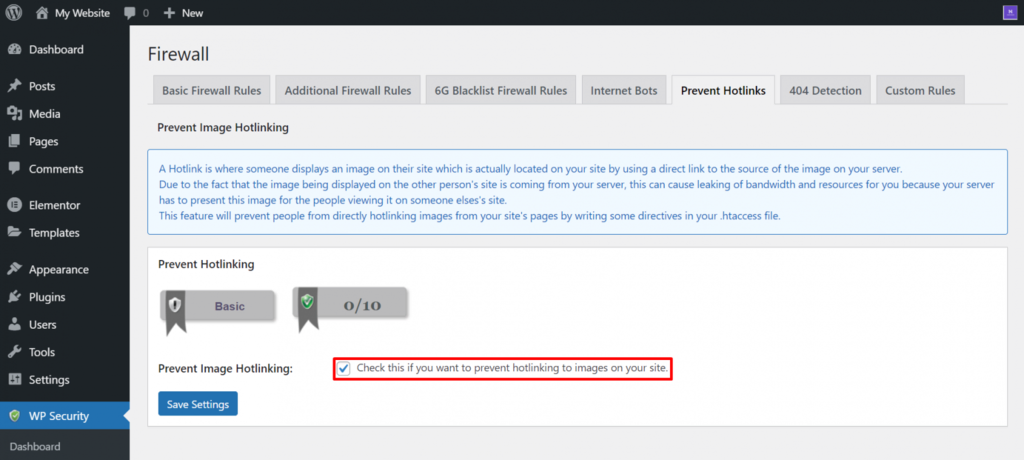
4. Click Save Settings.
Another plugin you can use is WP Content Copy Protection & No Right Click. This plugin can block visitors from copying text and right-clicking on your website. If you enable the right-click prevention, your visitors won’t be able to find or save the direct link to your content files.
Here’s how to enable the right-click protection on your site using this plugin:
- Install and activate the plugin.
- Click Copy Protection from your WordPress dashboard’s sidebar.
- Select the Premium RightClick Protection tab.
- Select the types of pages where you want to enable right-click protection. You can allow it on Posts, the Homepage, and other Static pages.
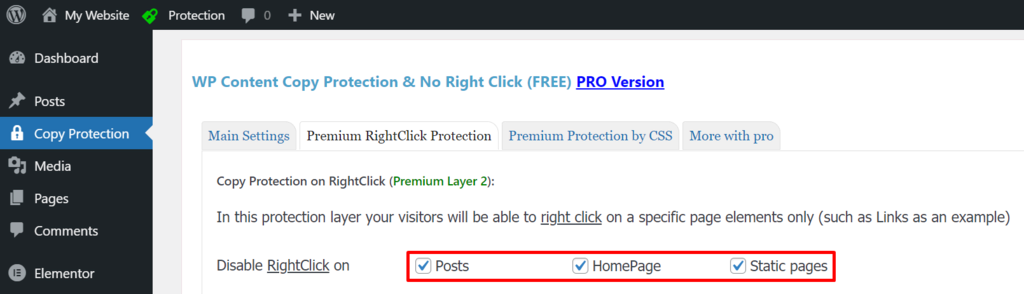
5. Click Save Settings.
Secure Copy Content Protection and Content Locking is another option to disable right-click and asset copying. Here’s how to set it up:
- Install and activate the plugin.
- From the WordPress dashboard, navigate to Copy Protection -> Options.
- Make sure that both Disable right-click and Disable right-click for images are ticked. Tick Show Message to give your visitors a message when they attempt to right-click on your site.
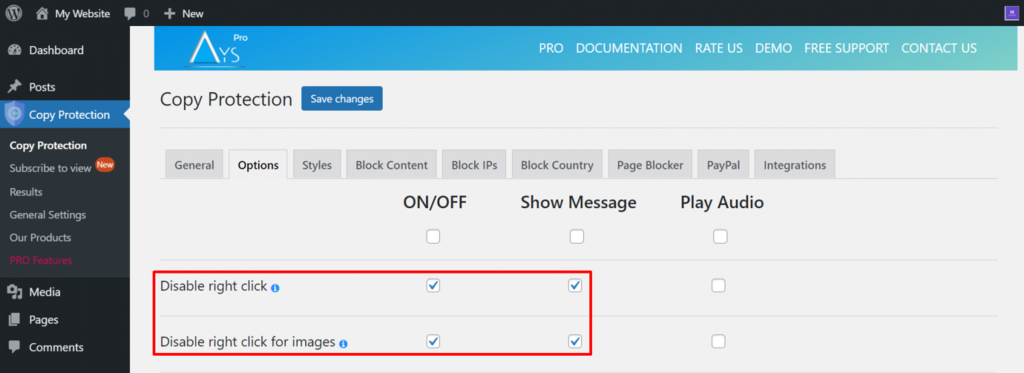
4. Click Save Changes.
Conclusion
Hotlinking is the act of copying assets, usually images, by linking the file directly from other websites without authorization.
It is a bad practice that negatively impacts web administrators. Hotlinking another website’s images can take up a significant amount of bandwidth on its server and infringe on its owners’ copyright.
We’ve explored different reasons why you should never hotlink and what you can do instead to obtain and share content assets. We also went over four methods to protect your website from hotlinking.
We hope that this article has helped you find better ways to acquire content and keep your site safe from bandwidth theft. Good luck.